Pest and Disease Control and Management in Rice
1.Diagram
|
The growth and development of rice |
||||||||
|
Vegetative period |
Reproductive growth period |
|||||||
|
Seedling stage |
Tillering stage |
Jointing and ear differentiation stage |
Maturity stage |
|||||
|
Seedling stage |
Regreening stage |
Effective tiller stage |
Jointing stage |
Young ear differentiation stage |
Booting stage |
Milk stage |
Dough stage |
Full ripe stage |
The Life History of Rice
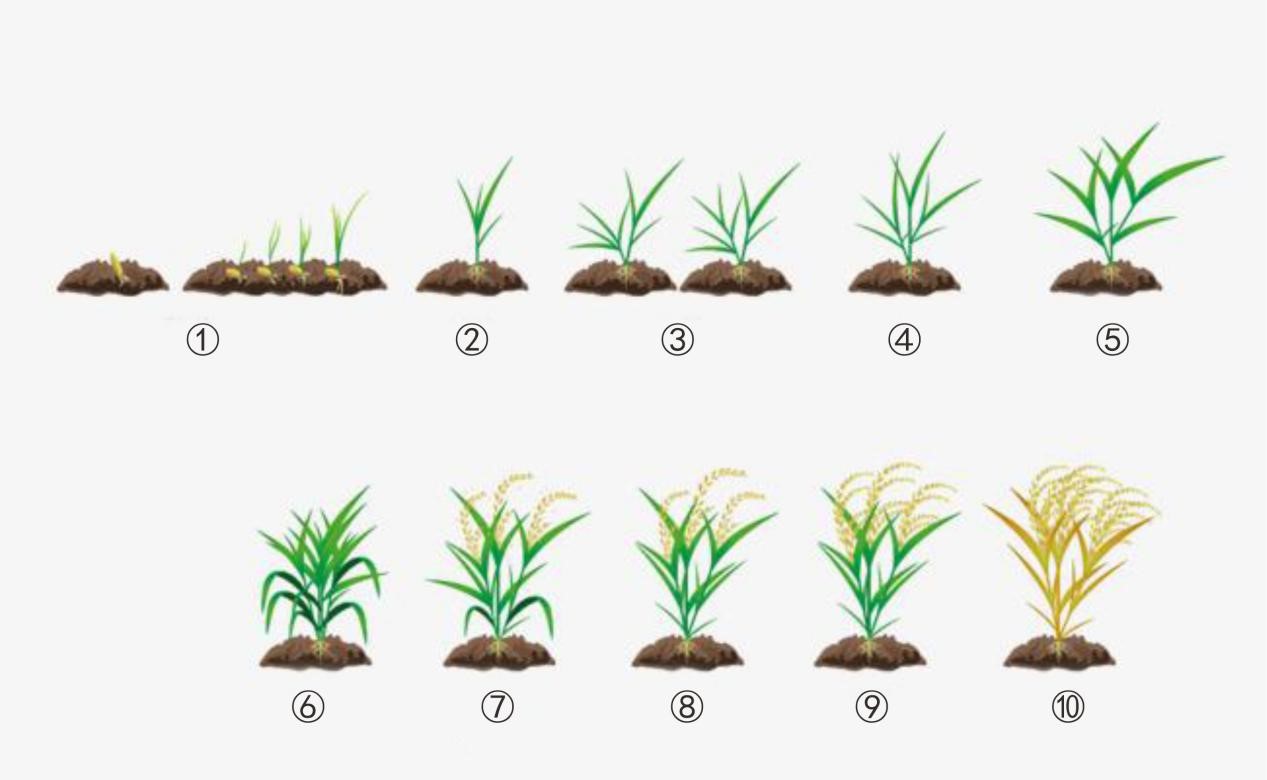

Picture Interpretation
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
|
Germination |
Seedling |
Tiller |
Jointing |
Booting |
Earing |
Flowering |
Milk ripeness |
Dough stage |
Full ripe |
2.Main characteristics of rice in each growth period
Generally, the growth period from seed germination to the production of new seeds is the growth period of rice. The growth period can be divided into seedling period, regreening period, tillering period, ear differentiation period, and fruit setting period.
2.1 Seedling stage: the stage from seed germination to the three-leaf stage.
Bud stage management
The budding period is from sowing to the first full leaf unfolding. The management of the bud stage is mainly to prompt the sprouted grain to quickly take root and erect needles to prevent the buds from falling and rotten. Sowing in sunny days, draining and drying the fields, etc.
Seedling management
The seedling stage is from one leaf spreading to three leaves. When the seedlings grow to the 3-leaf stage, the nutrients stored in the seeds are completely exhausted and turned into independent nutrition, which is called weaning stage. When the rice seedlings reach the three leaf stage, all the nutrients in the grains are exhausted, and all the nutrient sources need to be absorbed and manufactured by themselves,Before that, quick-acting fertilizer should be applied to supply nutrients. It is necessary to apply "weaning fertilizer" twice in advance during the 1 leaf 1 bud stage and the 2 leaf 1 bud stage respectively, and apply 3 to 4 kg of urea per mu; Apply tillering fertilizer at 2.5-3 leaf stage, and apply 4-5 kg urea per mu; Only when it is applied in advance can it be used in time, and it will be late when it is applied in the three leaf stage,it is already a fertilizer for promoting tillering, and cannot play the role of supplementing weaning fertilizer.
"Weaning fertilizer" refers to the top dressing of rice seedlings during the weaning period. It is directly related to whether the seedling can absorb nutrients from the soil normally. Usually the starch stored in the endosperm of rice seeds will not be exhausted until the three-leaf stage, so some people think that "weaning fertilizer" should be applied at the three-leaf stage. In fact, this is a misunderstanding. Studies have shown that "weaning fertilizer" should be applied early to the one leaf one bud stage, not the three leaf stage.
Attention should be paid during this period:
a. Weeds control (closed treatment of weeds that may appear in the future in advance)
b. The most common main diseases in rice seedling stage are damping off, bacterial wilt and rice blast, especially in abnormal climate, large temperature difference, obvious "cold in late spring" and low temperature year.
2.2 Tillering stage
Effective tillering: If the conditions are suitable after regreening, new plants can be extended from axillary buds of leaf axils at the base of false stems, which is called tillering. When 10% of the plants in the whole field tiller, it is the beginning of tillering; When 50% of the plants tiller, it is the peak period of tillering; When 80% of the plants stop tillering, it is the final tillering stage. When the number of tillers is equal to the number of ears grown by tillers, it is called effective tillering stage. Under normal circumstances, about 10 days after tillering begins, most of the tillers grow into ears.
Ineffective tillering: tillering which usually occurs after 20 ~ 25 days after transplanting, most of them stop growing in the middle and can't bear ears, which is actually a waste of nutrients, so it is called ineffective tillering. At this time, it is called invalid tillering stage. Therefore, in cultivation, effective measures should be taken to promote early tillering and multiple tillering before the effective tillering termination period, that is, within 20 days after transplanting; It is necessary to control ineffective tillering after effective tillering is terminated. Only in this way can rice have more ears and bigger ears, reduce the shade phenomenon in the field, and realize stable and high yield.
Attention should be paid during this period:
Prevention and treatment in advance. The control of rice blast is based on the leaf age process in the rice field. Simple broad-spectrum protective fungicides in the early stage. If such diseases occur in the field, use triazole fungicides such as tricyclazole and propiconazole for prevention and control.
2.3 Jointing and ear differentiation stage: jointing stage, young ear differentiation stage and booting stage
Jointing stage: The symbol of rice jointing is that the length of the first elongation joint at the base of rice reaches 1cm, and that of early rice and late rice is 2cm, and it changes from flat to round, which is the symbol of rice jointing. More than half of all rice in paddy field has entered jointing stage, which means that rice tillering has basically ended and started to enter the management stage of jointing stage.
Young ear differentiation and booting stage: Ear differentiation and jointing stage start almost at the same time, and there is no obvious time difference. The process from young ear differentiation to heading of rice is collectively called booting stage of rice.
Attention should be paid during this period:
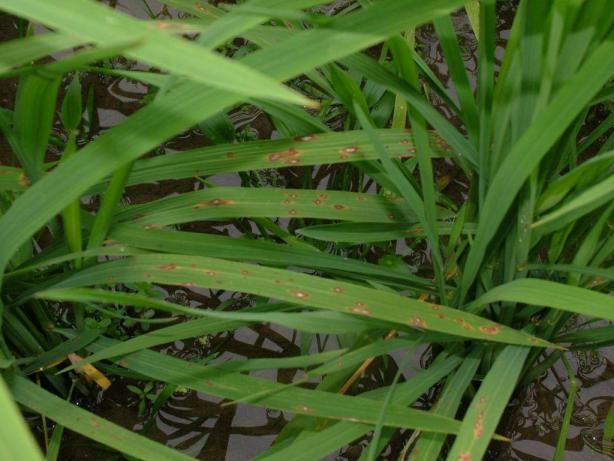


Rice blast
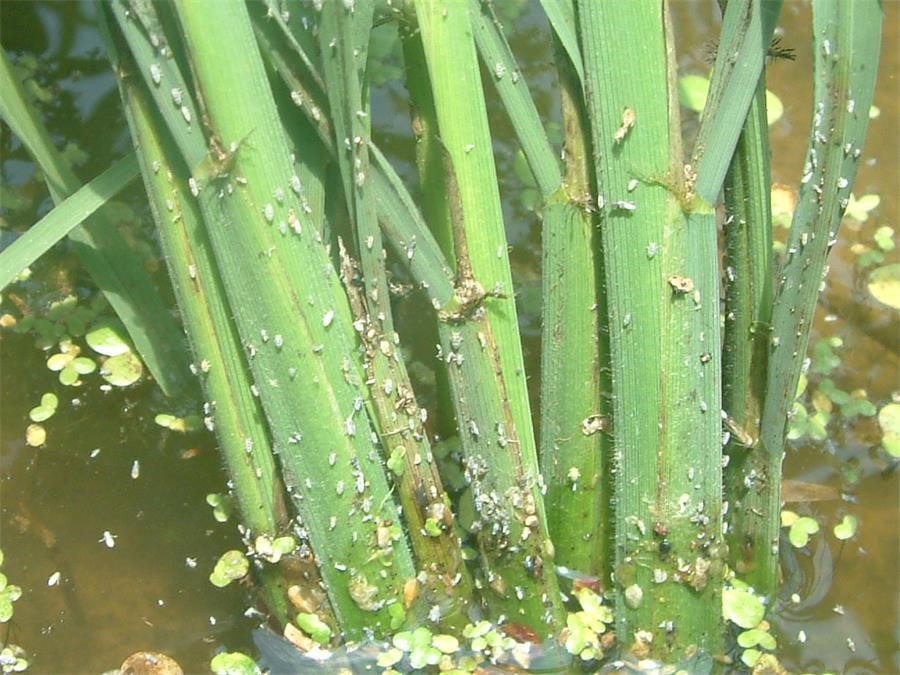
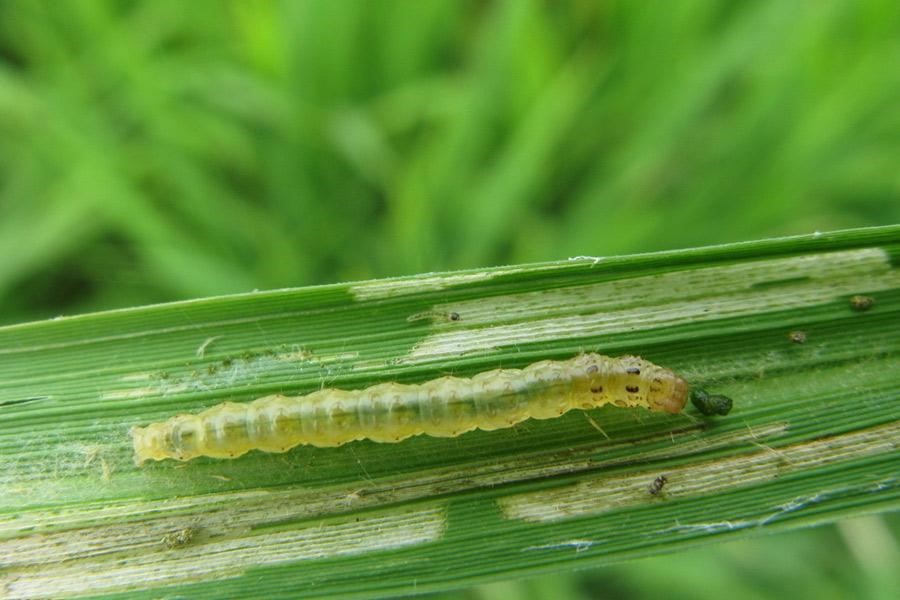


Rice planthopper Leaf roller
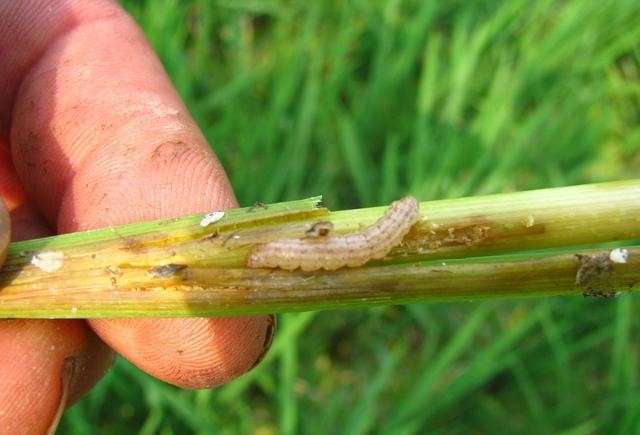


Sheath blight Borer
Comprehensive control,focusing on the occurrence of major rice diseases and insect pests such as rice blast, sheath blight, borer, leaf roller and rice planthopper. The weaker the crops, the more likely it is to get diseases.
2.4 Maturity stage: Milk stage, wax stage and full ripe stage
The heading and fruiting period of rice refers to the period from heading to grain maturity. Generally, it takes about 25~30 days for early maturing varieties, 30~35 days for middle maturing varieties and 40~45 days for late maturing varieties.
During this period, the growth of leaves stopped, the development of spikelets was completed, the elongation of stems reached the highest level after heading, and the growth center changed from ear differentiation in the previous stage to rice growth.
Attention during this period:
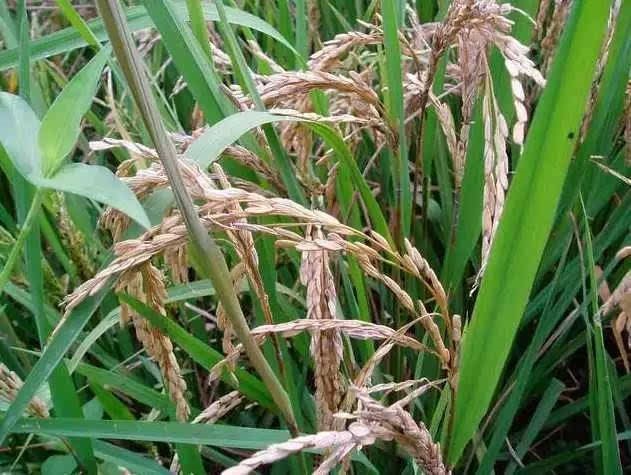
a. Leaf blight, sheath blight, rice neck blast, rice planthopper, armyworm and other diseases. Check frequently, and control pests and diseases in time if they are found.
b. Prevent and control weeds such as floating duckweed and moss in time, and removal of weeds in fields and ridges, so as not to block the light and affect the water temperature rise, but also reduce the weeds run riot in the next year and reduce the source of infection of diseases and insect pests.
c. According to the weather conditions, reduce the yield reduction caused by rice lodging.
3. Main pest control
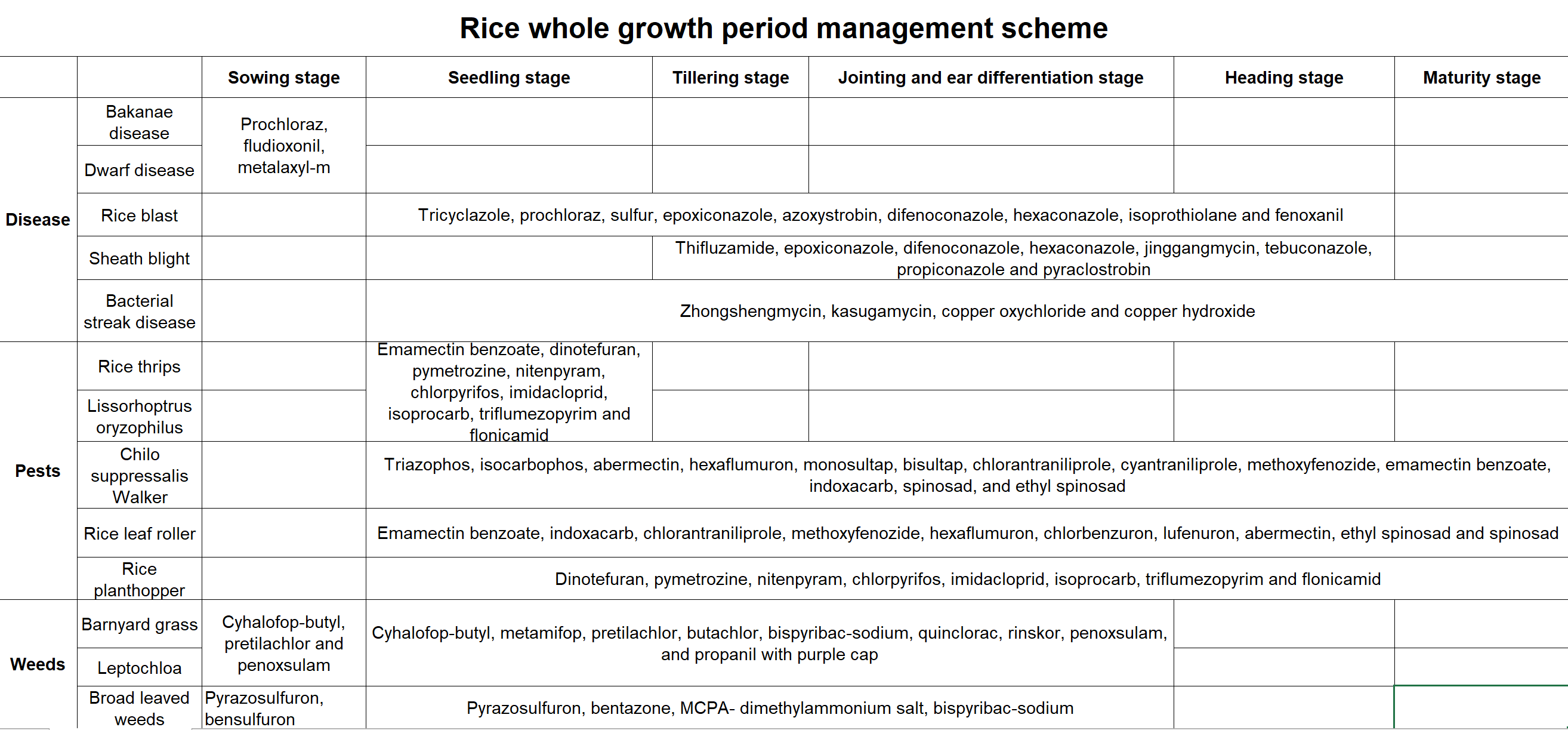
Major pests and diseases of rice: borer, leaf roller, rice planthopper, rice blast and sheath blight.
Weeds: According to the local weed situation, we mainly pay attention to barnyard grass, Leptochloa, sedge and annual broad leaved weeds.
Closed weeding: pretilachlor, butachlor, pyrazosulfuron, bensulfuron, pendimethalin, etc.
Borers: abermectin, chlorantraniliprole, hexaflumuron, lufenuron, isocarbophos, triazophos, acephate, monosultap, Cyantraniliprole, methoxyfenozide, etc.
Leaf roller: emamectin benzoate, indoxacarb, chlorbenzuron, chlorfenapyr, hexaflumuron, lufenuron, abermectin, etc.
Rice planthopper: nitenpyram, dinotefuran, pymetrozine, chlorpyrifos, isoprocarb, triflumezopyrim, imidacloprid, etc.
Rice blast: prochloraz, tricyclazole, propiconazole, tebuconazole, difenoconazole, azoxystrobin, pyraclostrobin, jinggangmycin, thifluzamide, isoprothiolane, etc
Sheath blight: prochloraz, tricyclazole, propiconazole, tebuconazole, difenoconazole, azoxystrobin, pyraclostrobin, jinggangmycin and thifluzamide.
4. Rice whole growth period management scheme

Tel: +86-21-58357653

Trading Office: Room 1201, Building B,Yujing International Business Plaza,No. 555 Pudong Avenue, Pudong,Shanghai,China.

E-mail: oreo.yum@oasisagro.com
About us
Stay with Oasis and find easier way to cultivate



Solutions

