PRODUCTS
Control of Main Grape Diseases (5)
Control of Main Grape Diseases (5)
Grape leafhoppers
Symptoms
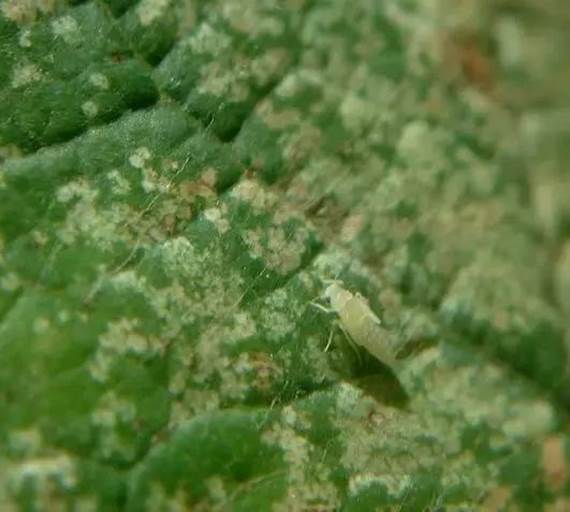

Adults and nymphs feed on leaves by puncturing the leaf cells and sucking out the contents. Each puncture causes a white blotch to appear on the leaf. Feeding causes leaves and fruit to appear stippled with many tiny white spots. Eventually, these spots turn brown and may cause leaves to drop prematurely. Leaves may become pale yellow in color and assume a sickly appearance. Feeding by leafhoppers may reduce the photosynthetic capacity of the plant, and the quality and quantity of the fruit may be affected.
Chemical control
Deltamethrin, fenvalerate, beta-cypermethrin, acetamiprid, imidacloprid.
Grape gall mites
Symptoms
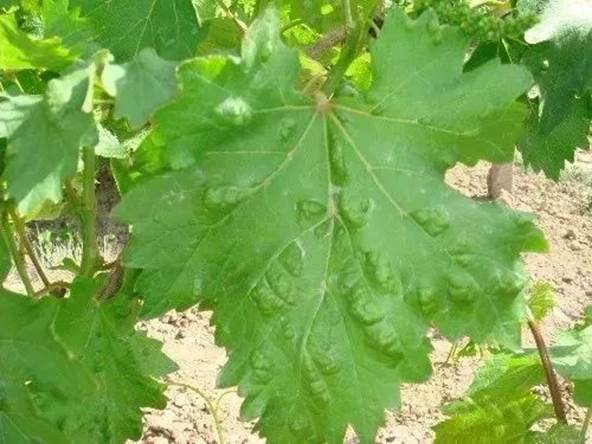
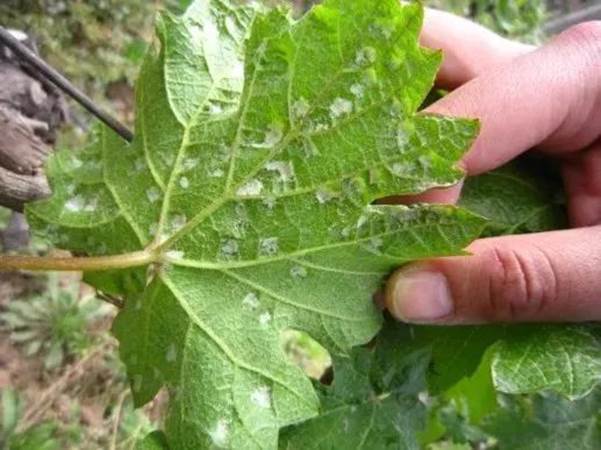


Grape gall mites are a species of tiny mites that dwell inside cracks along stems and under buds during the winter and emerge during the beginning of vegetative growth. Grape gall mites feed on the underside of leaves and cause the formation of thick white hair-like bunches that turn red-brown as time progresses. The most noticeable symptom of an infestation is the creation of galls on the upper side of leaves. Grape gall mites rarely cause significant damage to the vines, although it may cause the overall appearance of plants to be less aesthetic.
Chemical control
Clofentezine, fenpyroximate, liuyangmycin, azadirachtin, pyridaben, hexythiazox, acaricide.
Apolygus lucorum
Symptoms
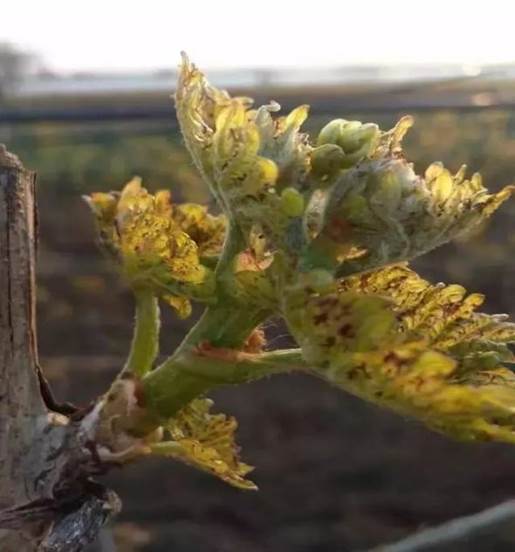
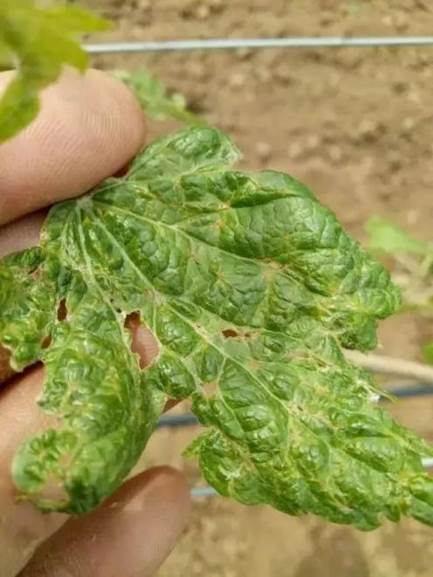


The injured leaves are reddish brown with necrotic spots the size of needles.
Irregular holes and wrinkles appear as the leaves grow.
Control
(1) clear the garden in time in winter and early spring;
(2) Spray 3~5 baume degrees of stone sulfur mixture before germination. Spraying pyrethroid pesticides such as imidacloprid and lambda-cyhalothrin at germination stage, paying special attention to early prevention and control of newly planted vineyards.
(3) Intercropping grapes with cotton and vegetables, strengthening pest control of crops around vines, thus reducing grape pests.
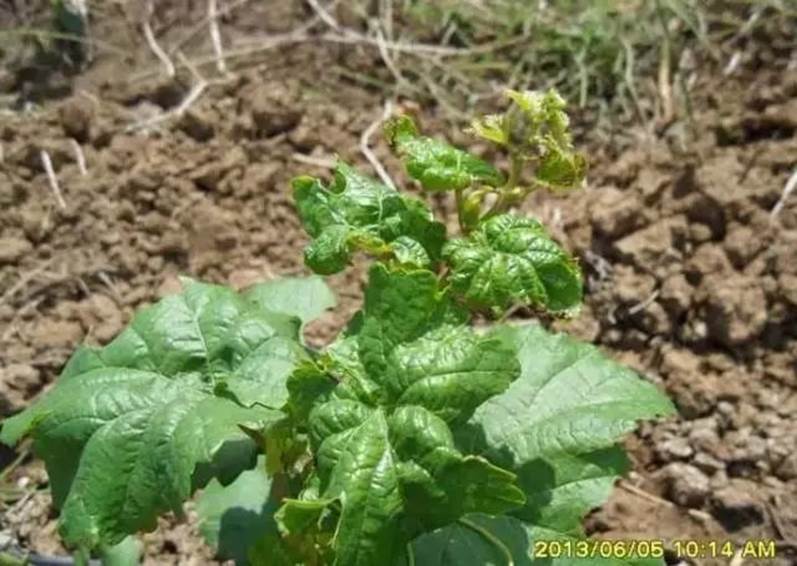
Grape thrips
Symptoms
Mainly suck the juice of grape buds and young fruits.
Damaged leaves appear small grayish-yellow spots, which affect growth and development and reduce yield in severe cases.
Leaves shrunken and inverted, with dark brown spots.

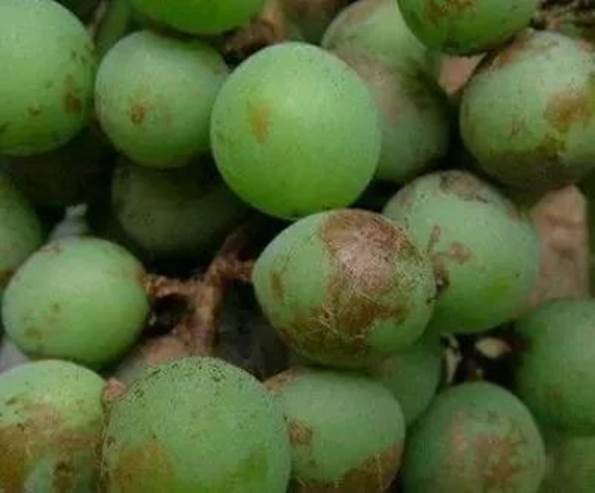
Dark brown spots appear on the peel, which are slightly sunken, nearly round or strip-shaped.

Chemical control
Beta-cypermethrin, acetamiprid, abamectin, tolfenpyrad.
Lycorma delicatula
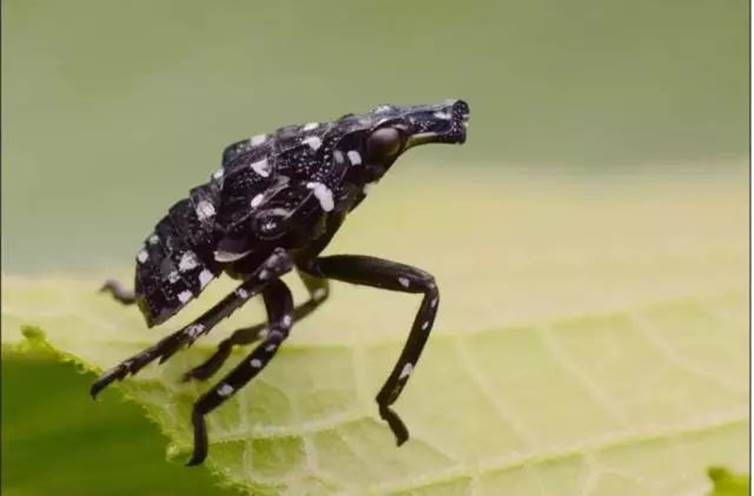

Symptoms
Nymphs and adults suck the juice of branches and leaves.
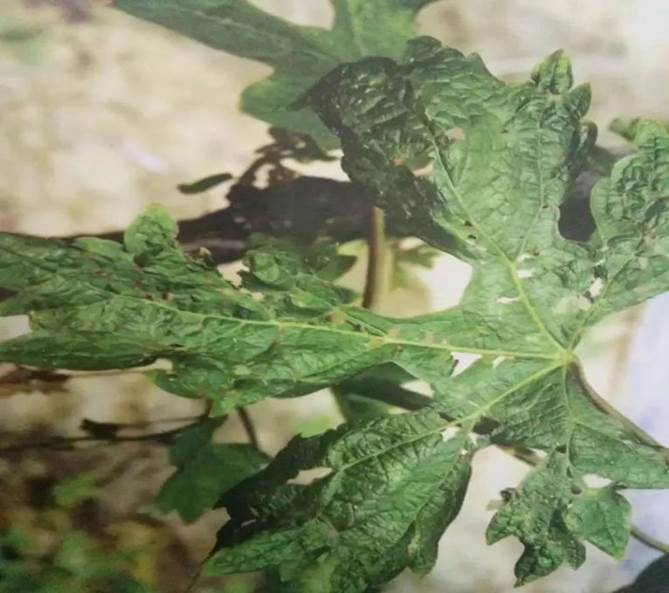
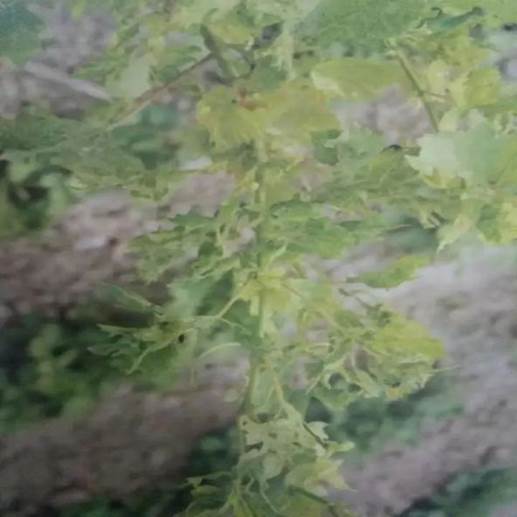


The damaged leaves formed pale yellow spots, which caused perforation and rupture in severe cases.
Harm the branches and blacken the branches.
Chemical control
Cypermethrin, deltamethrin, fenvalerate, imidacloprid, acetamiprid.
Grape phylloxera
Symptoms
It mainly harms leaves and roots.
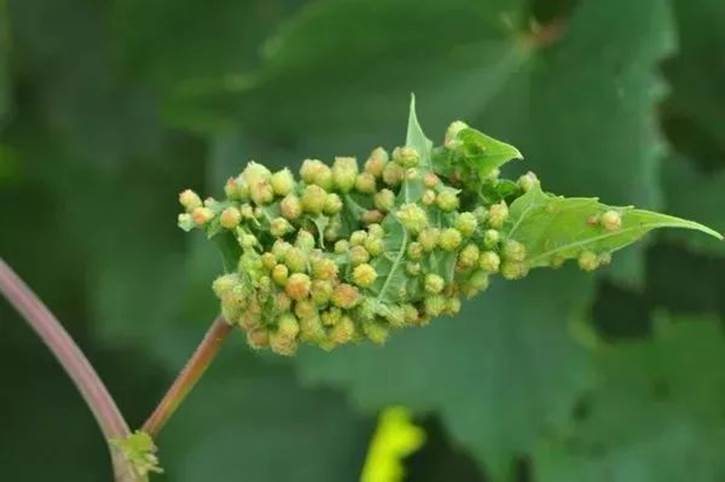

Many granular galls are formed on the back of grape leaves after the leaves are damaged, which is called "leaf gall type".
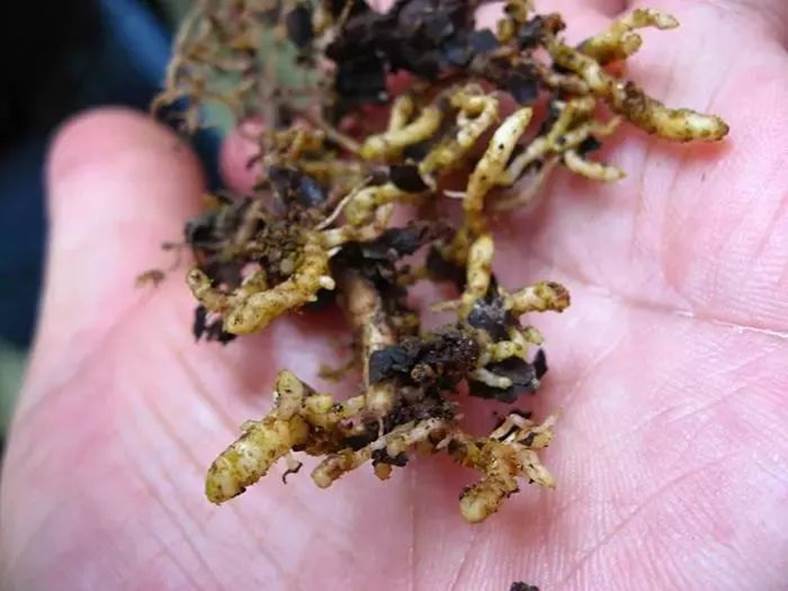

The damaged roots are mainly new fibrous roots or taproots near the ground.
The end of fibrous root swells into a slightly rhombic nodular knot which is slightly larger than that of millet, and a larger nodular protrusion is formed on the taproot, which is called "nodule type".
Generally, the affected vines are obviously weak, the leaves are yellowed and fall in advance, the yield is greatly reduced,and the whole plant dies in severe cases.
Chemical control
Beta-cypermethrin, lambda-cyhalothrin ·imidacloprid, spirotetramat.
Oides decempunctata
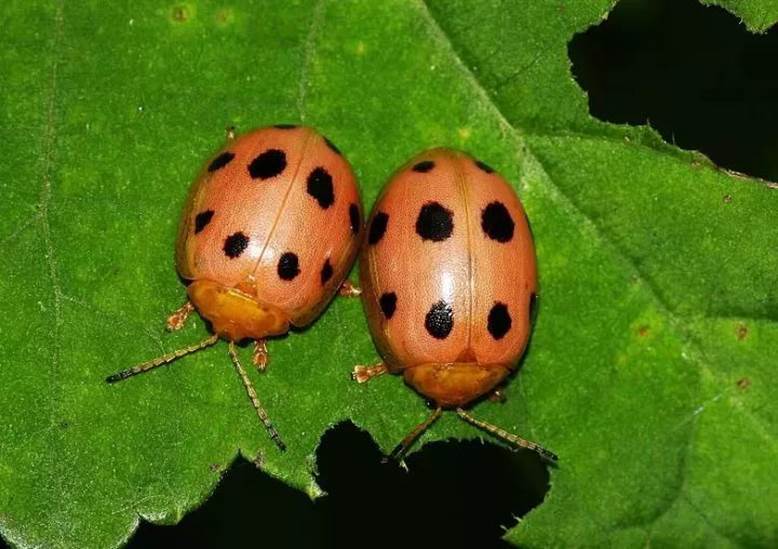 Symptoms
Symptoms
Larvae and adults feed on grape buds and leaves, resulting in many holes in the leaves. In severe cases, all the mesophyll is eaten up, leaving only some petioles and leaf veins.
Chemical control
Imidacloprid, monosultap, deltamethrin, thiamethoxam, fenvalerate.





 LANGUAGE
LANGUAGE